Recently, NVIDIA’s newly released GeForce RTX 5070 Ti has been reported to have hardware defects in some units, with the primary issue being a lower number of Raster Operation Units (ROPs) than officially specified. This problem is not limited to the RTX 5070 Ti but also affects high-end models like the RTX 5090 and 5090D, sparking widespread discussion within the community.
According to GPU-Z screenshots shared by users on social media, some RTX 5070 Ti units feature only 88 ROPs instead of the advertised 96, a reduction of approximately 8.4%. ROPs are a critical component in the GPU rendering pipeline, directly influencing pixel fill rate and overall graphics performance. Official data indicates that an RTX 5070 Ti with 96 ROPs achieves a pixel fill rate of 287.7 GPixel/s. However, defective versions, operating at lower frequencies, only reach 223.7 GPixel/s. Even when boosting the clock speed to 2.99 GHz, the fill rate rises to just 263.12 GPixel/s—about 9% lower than the standard version. This suggests that performance gaps will be even more pronounced in graphics-intensive tasks.
NVIDIA has responded to the issue, acknowledging that approximately 0.5% of RTX 5090, 5090D, and 5070 Ti graphics cards suffer from insufficient ROP counts, resulting in an average performance drop of about 4%. However, the real-world impact varies by use case: in games or benchmarks heavily reliant on ROPs, performance could dip by as much as 11%, while in other scenarios, the difference might be barely noticeable. The company emphasized that this defect stems from a production anomaly, which has since been resolved, and advised affected users to contact their board partners for replacements. Although 0.5% may seem minor, given the shipment volume of the RTX 50 series, this could still translate to thousands of affected cards.
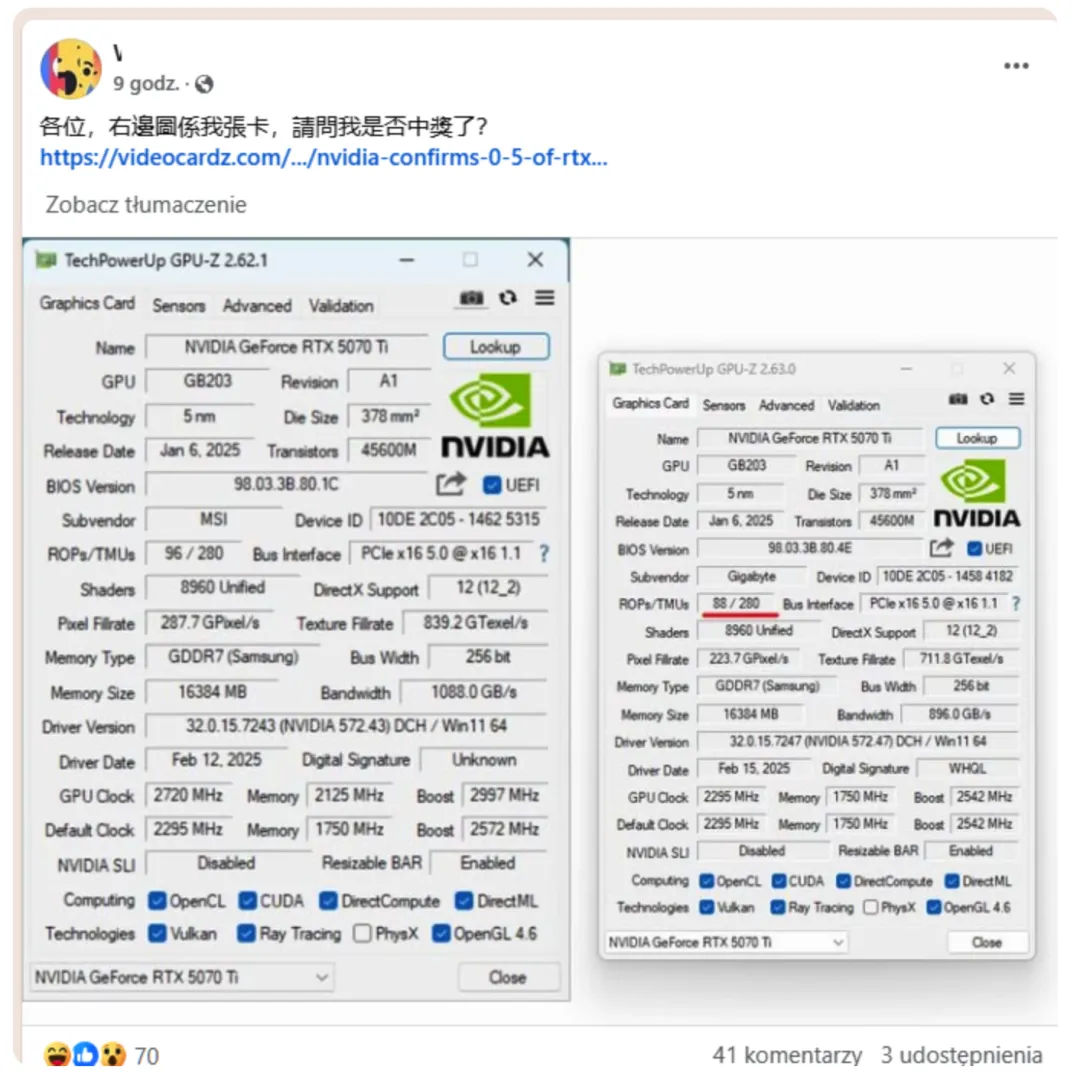
The RTX 5070 Ti is based on NVIDIA’s latest Blackwell architecture, featuring 8,960 CUDA cores, 70 RT cores, and 16GB of GDDR7 memory with a bandwidth of 896GB/s, positioning it as a high-end gaming option. Priced at $749 (6,299 RMB in China), it’s slightly cheaper than its predecessor, the RTX 4070 Ti Super ($799), making it an attractive choice. However, the ROP defect casts a shadow over the product’s reliability. Users can easily check their card’s ROP count using GPU-Z—if it’s below 96, it’s a defective unit.
Compounding the issue is the strained supply situation for the RTX 50 series. For instance, a Thai retailer has informed customers that, due to stock shortages, models like the RTX 5070 Ti may not arrive until July 2025. This exacerbates consumer concerns: even if a defective card is identified, replacement could be delayed indefinitely due to limited availability. Additionally, reports have surfaced of RTX 5090 users experiencing melted power connectors, suggesting that purchasing these new models carries some risks.
From a technical perspective, fewer ROPs directly weaken a card’s rendering capabilities, with the impact most noticeable in high-resolution gaming (e.g., 4K) and full ray-tracing scenarios. Take the popular game Cyberpunk 2077 as an example: with full ray tracing and DLSS 4 enabled, a standard RTX 5070 Ti can deliver smooth frame rates at 1440p, while a defective version might suffer from additional latency or frame drops. NVIDIA has claimed that the RTX 5070 Ti, bolstered by DLSS 4’s multi-frame generation technology, doubles the performance of its predecessor.
Notably, the RTX 5070 Ti isn’t an isolated case. The RTX 5090 has also been reported to have its ROP count reduced from 176 to 168, with a performance drop similar to that of the 5070 Ti. This issue highlights potential weaknesses in NVIDIA’s production and quality control processes. While the company insists that the affected units represent a tiny fraction and have negligible impact on AI or compute tasks, for users seeking the ultimate gaming experience, any performance compromise is unacceptable.

The RTX 5070 Ti officially launched on February 20, 2025, alongside the RTX 5090 and 5080, forming the initial lineup of the Blackwell series. The standard version boasts 28Gb/s GDDR7 memory, a 256-bit memory bus, and support for the latest DisplayPort 2.1a and HDMI 2.1b interfaces, with a power consumption of around 300W. Compared to the RTX 4070 Ti Super (285W), its performance gains stem primarily from architectural improvements and AI enhancements. However, the ROP defect revelation may push some consumers to wait for the upcoming RTX 5070 or consider AMD’s competing Radeon RX 9070 XT.
How NVIDIA handles inventory and replacement processes moving forward will be a key test of its after-sales service. Facing both supply constraints and a hit to consumer trust, the Blackwell series is off to a rocky start.
